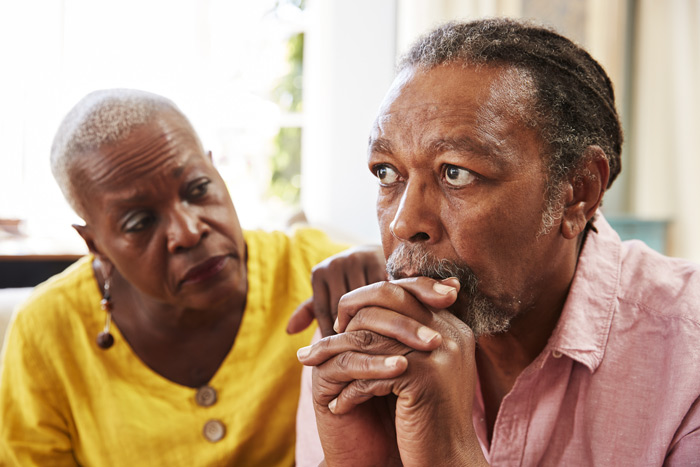

Navigating the Shadows: Understanding Depression in Older Adults
Introduction
As we age, life brings new challenges and experiences. For many older adults, the golden years can be a time of reflection, fulfillment, and a chance to enjoy the fruits of their labor. However, this stage of life is not without its difficulties. Depression, a condition often associated with younger individuals, can also impact older adults in profound ways. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of depression in older adults, shedding light on its causes, signs, and the importance of addressing it with compassion and care.
The Prevalence of Depression in Older Adults
Depression among older adults is more common than many might assume. Facing various life changes such as retirement, loss of loved ones, declining health, and social isolation, seniors can be susceptible to depression. According to the World Health Organization, around 7% of adults over the age of 60 experience a mental health disorder, with depression being one of the most prevalent conditions.
Contributing Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of depression in older adults:
1. Loss and Grief: The loss of a spouse, close friends, or family members can be emotionally devastating, leading to feelings of loneliness and grief that may trigger or exacerbate depression.
2. Health Issues: Physical ailments, chronic illnesses, and declining mobility can significantly impact an older adult’s quality of life and contribute to feelings of hopelessness and sadness.
3. Social Isolation: As social circles shrink, older adults may find themselves increasingly isolated, leading to feelings of loneliness and a lack of purpose.
4. Financial Stress: Worries about financial stability during retirement can create anxiety and emotional distress, potentially leading to depression.
Recognizing the Signs
Recognizing depression in older adults can be challenging, as symptoms may manifest differently than in younger individuals. Some common signs of depression in seniors include:
1. Persistent Sadness: An overwhelming and long-lasting feeling of sadness, hopelessness, or emptiness.
2. Loss of Interest: A lack of interest or pleasure in activities that the individual once enjoyed, including hobbies, social gatherings, and family events.
3. Changes in Appetite: Significant weight loss or gain, as well as changes in eating habits.
4. Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia or excessive sleep that disrupts regular sleep patterns.
5. Fatigue and Low Energy: Feeling constantly drained and having little motivation to engage in daily activities.
6. Cognitive Changes: Difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and reduced decision-making abilities.
7. Physical Complaints: Frequent complaints of unexplained aches, pains, and physical discomfort.
The Importance of Addressing Depression in Older Adults
Depression in older adults is not just a natural consequence of aging; it is a serious medical condition that requires attention and care. Failing to address depression can have severe consequences, both physically and emotionally, impacting an older adult’s overall well-being and quality of life. Untreated depression can lead to social withdrawal, worsening physical health, cognitive decline, and an increased risk of suicide.
Breaking the Stigma
Unfortunately, depression and mental health concerns among older adults are often overlooked or dismissed as merely a part of getting older. It is crucial to break this stigma surrounding mental health in the elderly and treat depression with the same seriousness as any other medical condition.
Supportive Interventions
Several interventions can help older adults manage and overcome depression:
1. Open Dialogue: Encouraging open conversations about mental health allows older adults to express their feelings and emotions without judgment.
2. Professional Support: Seeking help from mental health professionals, such as therapists or counselors, can provide effective coping strategies and emotional support.
3. Medication: In some cases, antidepressant medication may be prescribed to alleviate the symptoms of depression in conjunction with therapy.
4. Engaging Activities: Encouraging participation in social activities, hobbies, or volunteering can combat feelings of isolation and boost overall well-being.
5. Exercise: Regular physical activity has proven benefits for mental health, as it releases endorphins and reduces stress.
Promoting Social Connections
Promoting social connections among older adults is vital in combating depression. Community centers, senior clubs, and intergenerational programs can foster a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation. Additionally, technology can be harnessed to connect seniors with friends and family, especially if distance is a limiting factor.
Conclusion – Depression in Older Adults
Depression in older adults is a serious and prevalent issue that deserves our attention and empathy. By understanding the factors that contribute to depression in seniors, recognizing the signs, and promoting supportive interventions, we can work towards creating a more compassionate and inclusive society for older adults. Nurturing social connections, breaking the stigma surrounding mental health, and providing access to professional support are essential steps in helping older adults navigate through the shadows of depression and embrace the golden years with renewed hope and resilience.





1 thought on “Depression In Older Adults”
Great article!